In-Space Production Applications
IN-SPACE PRODUCTION APPLICATIONS
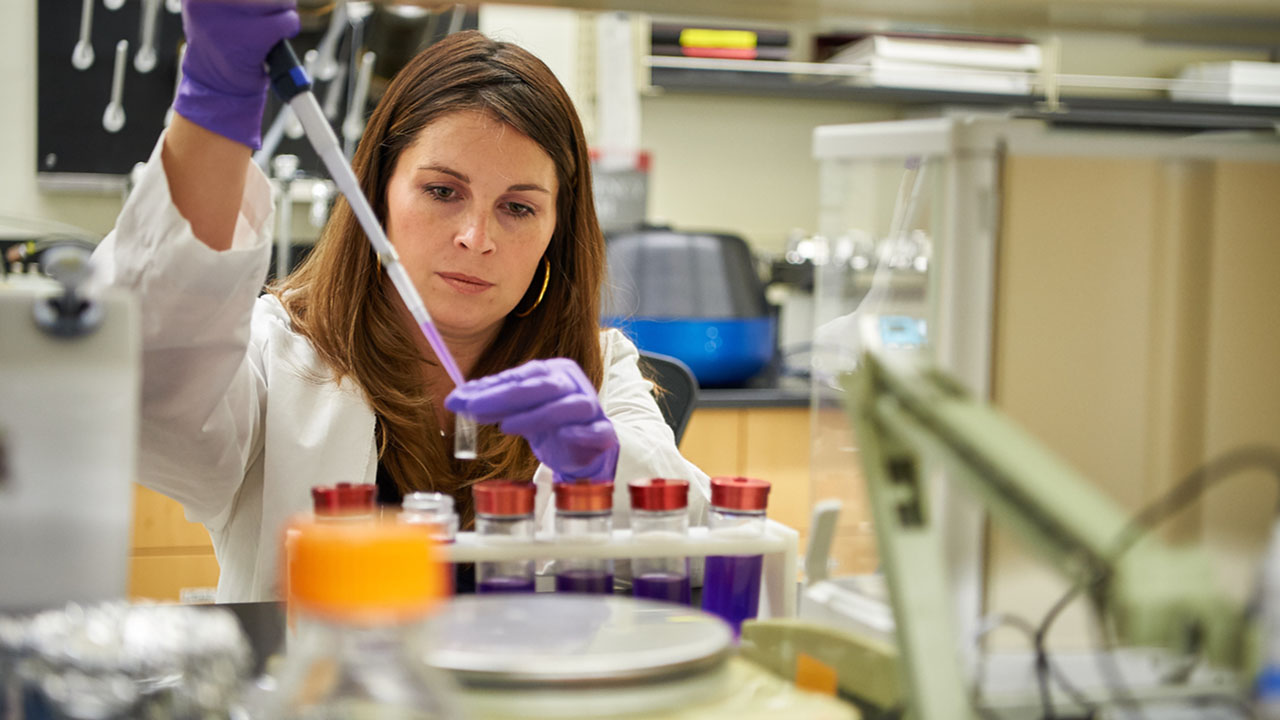
The International Space Station (ISSInternational Space Station) serves as a unique research and development (R&D) environment to develop products in space that cannot be realized on Earth. Researchers in the area of in-space production applications(Abbreviation: InSPA) InSPA is an applied research and development program sponsored by NASA and the ISS National Lab aimed at demonstrating space-based manufacturing and production activities by using the unique space environment to develop, test, or mature products and processes that could have an economic impact. will apply knowledge gained from past space-based research to develop, demonstrate, and master in-space production and manufacturing to specific performance standards in multiple high-tech application areas worthy of public investment to help scale and transition these efforts to industrial partners.
Projects within in-space production applications will inform and open new classes of materials, applications, and products that advance existing space-based research successes and ultimately product development. In-space production applications research is poised to bridge the gap between discovery and application, addressing the “valley of death” between lab-based research and the creation of a successful product, medical treatment, manufacturing process, or new and improved material. The in-space production applications effort is expected to evolve as projects develop through annual open, peer-reviewed solicitation opportunities.
The ISS National Lab defines in-space production applications as:
Low Earth orbit(Abbreviation: LEO) The orbit around the Earth that extends up to an altitude of 2,000 km (1,200 miles) from Earth’s surface. The International Space Station’s orbit is in LEO, at an altitude of approximately 250 miles. (LEO)-based applied R&D microgravityThe condition of perceived weightlessness created when an object is in free fall, for example when an object is in orbital motion. Microgravity alters many observable phenomena within the physical and life sciences, allowing scientists to study things in ways not possible on Earth. The International Space Station provides access to a persistent microgravity environment. applications seeking to demonstrate space-based manufacturing and production activities that enable new business growth and capital investment, represent scalable and sustainable market opportunities, and produce reoccurring value with the potential to generate demand for and revenue from access to space.
In-Space Production Applications Research Areas

Advanced Manufacturing & Materials
The absence of gravity and exposure to extreme conditions can affect fluid behavior and alter certain materials, improving our understanding of foundational processes and enabling the development of advanced materials and better manufacturing systems for use on Earth and in space.

Crystal Growth
Microgravity has been used for more than 30 years to improve outcomes of molecular crystal growth, and high-quality crystals of organic and inorganic molecules have valuable applications in drug development, agriculture, optics, electronics, and more.

Thin-Layer Deposition
Microgravity can improve the uniformity of layers in thin-layer deposition, the process of creating and depositing thin film coatings onto a substrate material with the ability to design in certain properties that improve the performance of the material.
Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine
In microgravity, cells form complex 3D structures, enabling the culture of tissues that more closely resemble those in the body for use in disease modeling, improved drug development analysis, regenerative medicine applications, and organ growth for wound healing and to address the shortage of organs for transplantation.







