Removing Gravity From the Manufacturing Equation

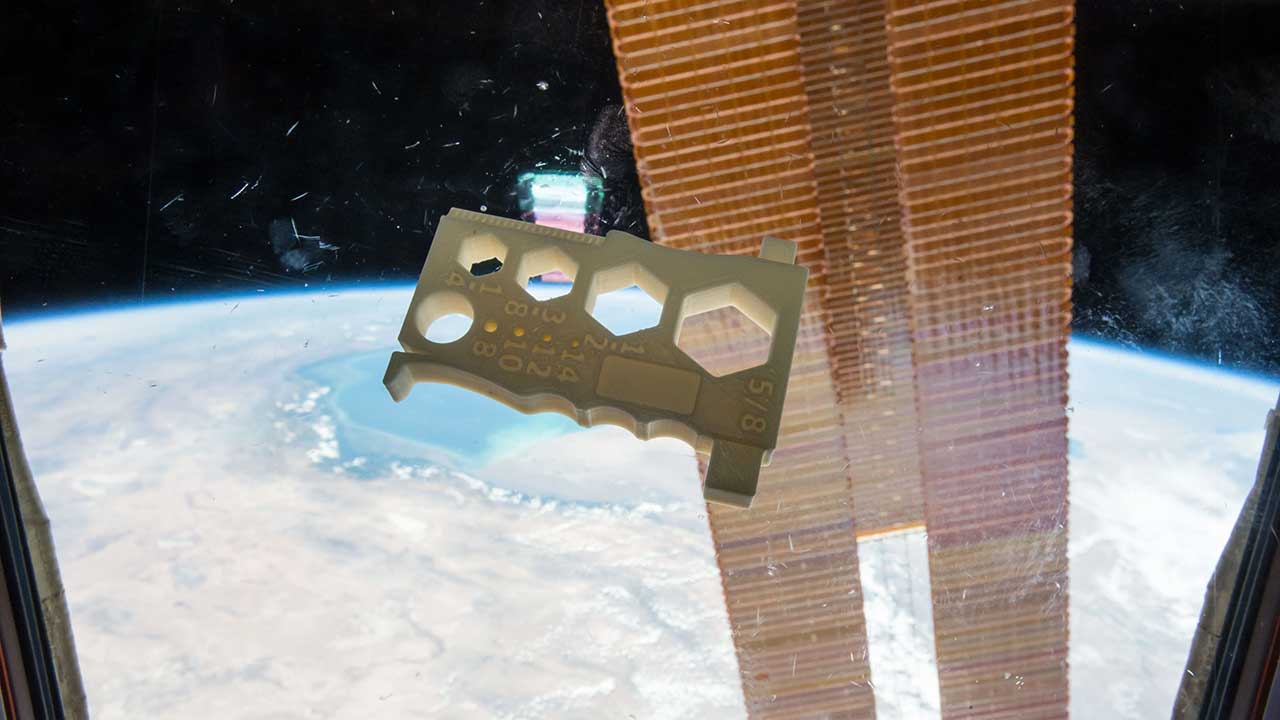
A space-optimized wrench for ISS crew members 3D-printed onboard the space station using the Additive Manufacturing Facility.
Media Credit: Made In Space
August 8, 2018 • By Andrew Rush, Guest Contributor, President of Made In Space, Inc. and Chief Operating Officer of Redwire
What if you could design and manufacture objects intended for space actually in space, rather than designing them to withstand a rocket launch first to get there? That’s the vision of Made In Space, Inc., and we’re producing parts, tools, and products in space right now using 3D printing technology on the International Space Station (ISS).
Taking Manufacturing Into Space
Since working with NASANational Aeronautics and Space Administration to put a prototype 3D printer onboard ISSInternational Space Station in 2014, we’ve been following a developmental trajectory that’s opened doors to a whole new way of thinking about everything from high-tech manufacturing to cutting-edge research onboard the ISS, deep space exploration, and even human habitation of the moon and other planets.
Once we’re free from the traditional build-and-transport model, the possibilities for manufacturing in space are virtually unlimited. Instead of paying to transport parts and build satellites and other spacecraft through astronaut extravehicular activity, parts for satellites, telescopes, and space stations can all be manufactured in orbit and assembled in their operational environment.
Although in-orbit manufacturing was once thought to be science fiction, we were able to make it a reality by bringing manufacturing technology to space and making it commercially viable. We were able to do this by developing an efficient and cost-effective process built around structured planning and testing combined with streamlined execution. In short, we created a road-map process for successful manufacturing in space.
From Conception to Demonstration
The initial concept was basic: To design a 3D printer that would work in space and send it to the space station to demonstrate that in-orbit manufacturing could be done. However, in the end, the concept evolved into not only a process we used to develop and demonstrate our technology but also a process that our customers could use to effectively design, test, create, and deliver their own tools, products, and structures.
In cooperation with NASA, we first validated our in-orbit 3D printing technology on parabolic flights. Then, to demonstrate the technology in space, we launched our prototype 3D printer to the ISS. Its validation served as a grand achievement for humanity and a “first” for off-Earth manufacturing. In 2016, the Additive Manufacturing Facility was installed onboard the ISS, providing a permanent commercial facility capable of producing larger, more complex objects.

We have successfully demonstrated an extensive set of manufacturing capabilities on parabolic flights, including metal casting and electronics printing that will enable space-based manufacturing of larger, stronger, and more complicated structures. We are also testing technology onboard the ISS for the production of high-quality ZBLAN optical fiber in space.
Via a private-public partnership with the NASA Space Technology Mission Directorate, these foundational technologies are also being used to develop in space manufacturing and assembly capabilities which will one day enable satellites and space stations to be robotically built and reconfigured in space!
We are excited as we move toward a bright future in commercial in-orbit manufacturing, and the potential of this new technology is only limited by the imagination of the humans who use it.
ISS Innovation Award
Made In Space was recently awarded the 2018 International Space Station Innovation Award in Physical Sciences and Materials Development at the 2018 ISS Research and Development Conference for their innovative work on ZBLAN optical fiber production in microgravity. Read more about the award and Made In Space’s in-orbit production of ZBLAN optical fiber here.